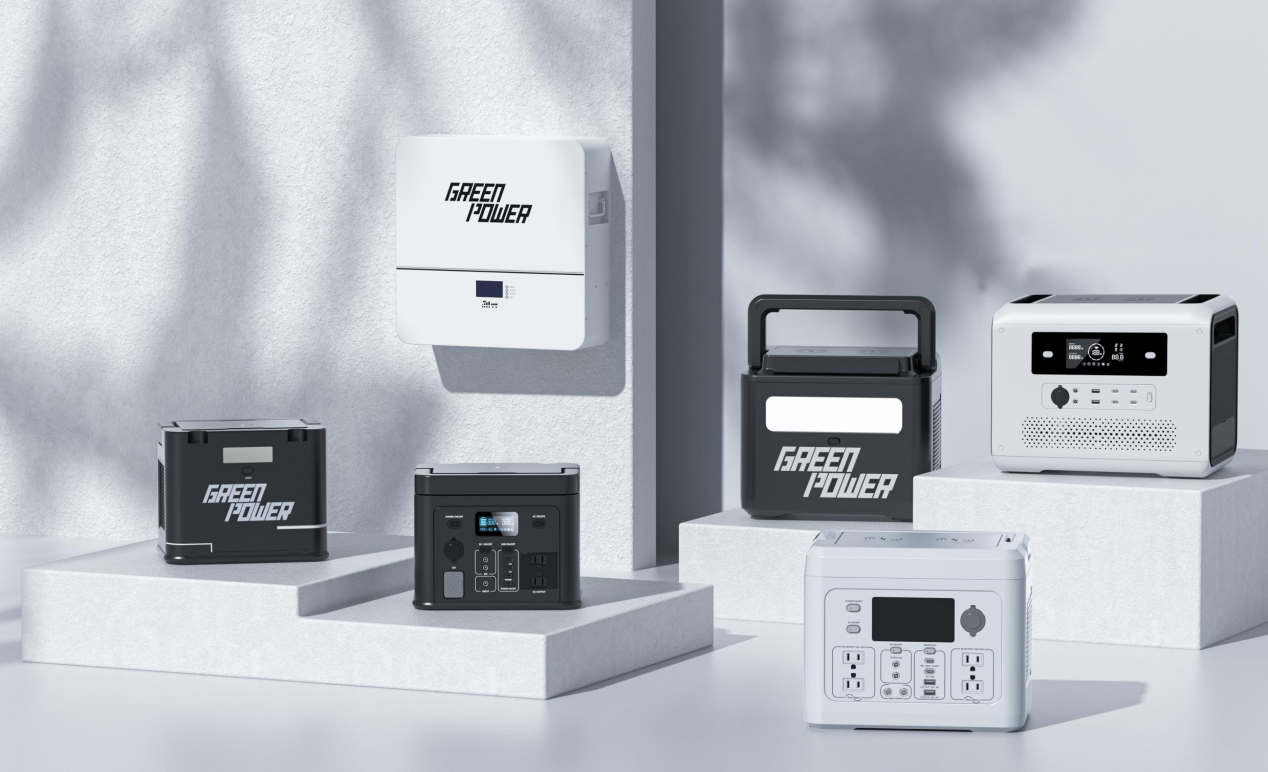
When selecting a battery, understanding key battery terms and concepts is crucial. This knowledge helps ensure that your power system can effectively meet your energy needs. Let's delve into these concepts and use real-world examples to illustrate the differences in battery parameters across various applications.
Capacity:
Capacity is the fundamental parameter for measuring a battery's ability to store and supply energy. Different types of batteries have significant differences in capacity. Let's discuss this in detail:
Portable Power Station: Suppose we consider a portable power station product named GREEN POWER MARS716 with a capacity of 32 ampere-hours (Ah). This means it can provide 32 Ah of electrical energy. For example, it can serve as a backup power source for devices such as smartphones and tablets for an extended period.
Home Energy Storage Battery: Home energy systems are typically used to store energy generated by solar panels to power a home during the night or on cloudy days. These batteries have a much larger capacity, typically ranging from 5 kilowatt-hours (kWh) to 20 kWh. For instance, a large home energy battery can store enough energy to support a day's worth of household electricity needs, including lighting, TV, refrigeration, and more.
Commercial and Industrial Energy Storage Battery: Large-scale commercial and industrial energy storage systems require even greater capacity to meet larger power demands. The capacity of these systems can range from several hundred kilowatt-hours (kWh) to several megawatt-hours (MWh) or more. For example, a large data center might utilize a 2 MWh energy storage system to maintain a continuous power supply and balance loads.
Battery Voltage:
Battery voltage is another crucial parameter, and different applications require varying voltage levels:
Portable Power Station: Typically, portable power stations operate at 22.4 volts (V) to support a variety of devices. This voltage level is suitable for mobile charging, camping, and outdoor activities.
Home Energy Storage Battery: Home batteries generally use a 48 V voltage to meet the requirements of household appliances and solar inverters. This voltage level is suitable for residential electricity.
Commercial and Industrial Energy Storage Battery: Large-scale energy storage systems often require higher voltages, ranging from several hundred volts (V) to kilovolts (kV), to meet larger energy demands. These systems are used in grid management, backup power for factories, and other large-scale applications.
Ampere-Hours (Ah):
Ampere-hours are used to measure a battery's capacity, and here are some examples:
Portable Power Station: A capacity of 32 Ah means it can provide 32 ampere-hours of current, or in other words, 32 Ah of electrical energy in one hour. This is sufficient for charging digital devices while also providing additional backup power.
Home Energy Storage Battery: Calculating the capacity for home batteries requires considering the battery voltage. For example, if the capacity is 20,000 watt-hours (Wh), and the voltage is 48 V, the capacity would be 20,000 Wh / 48 V = 416.67 Ah. This means it can continuously supply power for a certain period to meet a household's basic electrical needs.
Commercial and Industrial Energy Storage Battery: The calculation logic for industrial batteries is similar to that of home batteries and involves conversion based on voltage. These large battery systems can provide several hours or even a full day of backup power to industrial facilities.
Depth of Discharge (DOD):
Depth of discharge indicates how much energy can be used from the battery before it needs recharging. Here are some examples:
Portable Power Station: To extend the lifespan of the power source, it's generally recommended to avoid deep discharge. If the depth of discharge is 80%, and the battery capacity is 32 Ah, you can use 32 Ah * 80% = 25.6 Ah of energy before recharging. This is sufficient to support multiple recharges, suitable for outdoor activities and travel.
Home Energy Storage Battery: Home batteries are typically set at a depth of discharge of 70% to 80%, meaning you use only 70% to 80% of the capacity. This helps prolong battery life while meeting daily household electricity needs.
Commercial and Industrial Energy Storage Battery: Industrial-grade batteries typically support deeper depth of discharge, often up to 80% to 90%. This allows them to provide more backup power during peak electricity demand, reducing energy costs.
Efficiency:
Efficiency is crucial to understanding how much energy is lost during the charging and discharging process. Here are some examples:
Portable Power Station: If the efficiency is 90%, and you charge the battery with 1,000 watt-hours (Wh) of energy, the actual usable energy will be 1,000 Wh * 90% = 900 Wh. This means there is some energy loss during the energy conversion process.
Home Energy Storage Battery: Home batteries typically exhibit high efficiency, often exceeding 90%. This means minimal energy loss, allowing the battery to efficiently store and release energy, providing reliable power for homes.
Commercial and Industrial Energy Storage Battery: Larger-scale systems can achieve higher efficiency, typically ranging from 95% to 98%. This is particularly critical for large industrial applications, as energy loss can lead to high energy costs.
In conclusion, understanding these battery parameters and their calculation logic is essential for designing reliable and efficient energy storage systems. Whether you are concerned with portable power stations, home energy storage batteries, or commercial and industrial energy storage batteries, the right battery parameters and calculation logic play a crucial role in meeting your specific energy needs.
Cycle:
Every time a battery is discharged and then recharged, that's one cycle. The bestway to estimate the true life of a battery isn't based on time (for example, a 3-year warranty) but by estimated cycle life-the number oftimes a battery can charge and discharge overthe course of its lifespan.
Optimizing Your Energy System:
Once you grasp these key battery terms and concepts, you can better optimize your energy system. Whether it's providing backup power for your smartphone, supporting household appliances, or ensuring a stable power supply for industrial facilities, choosing and configuring the right batteries will improve energy efficiency and reduce energy costs. If you need advice or assistance, feel free to consult professional energy system experts who can provide customized solutions tailored to your needs.
If you're interested in learning more about our solar energy storage offerings, we encourage you to explore our product line. We offer a range of panels and battery that are designed for various applications and budgets, so you're sure to find the right solution for your needs.
Email:Info@fgreenpv.com
WhatsApp:+86 17311228539
Post time: Oct-16-2023