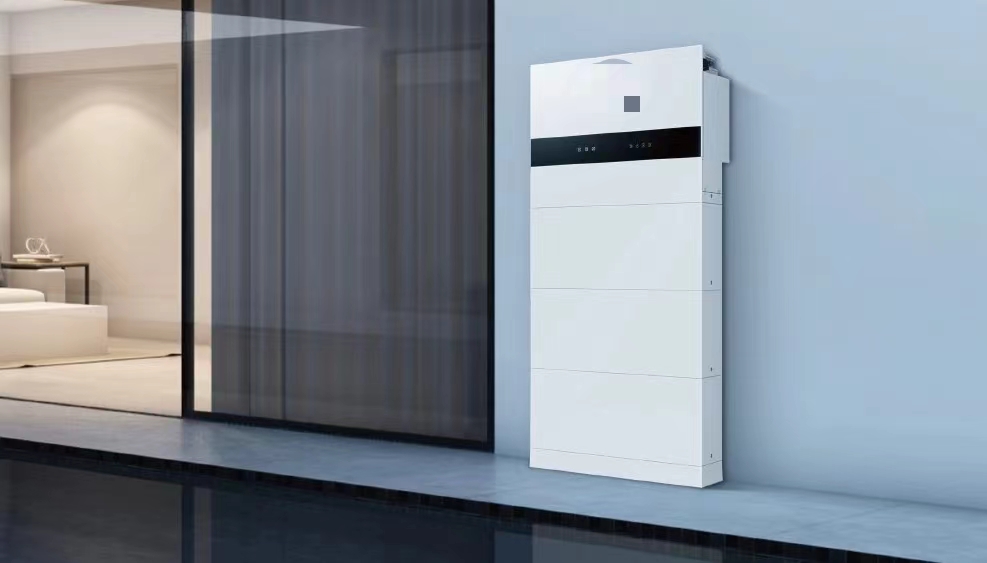
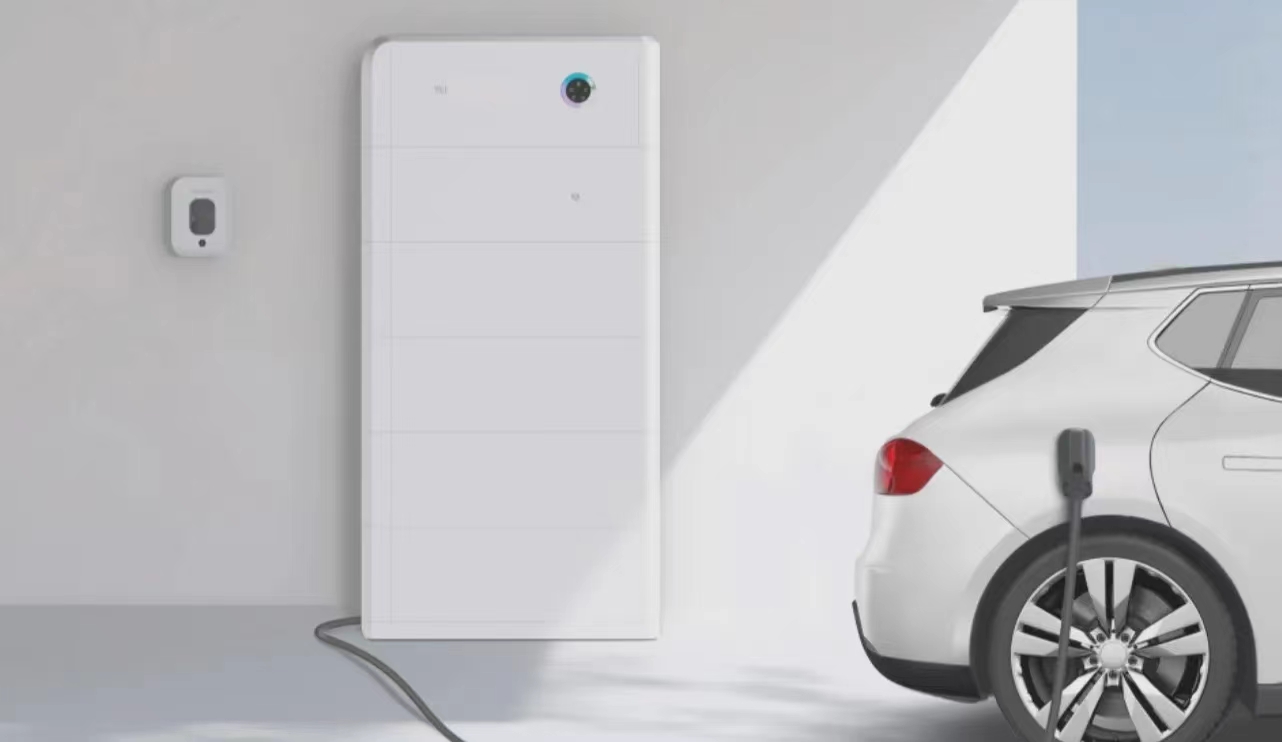
Let’s cut to the chase—solar power is awesome, right? It’s clean, it’s renewable, and it’s become a total workhorse in the global shift to greener energy. But here’s the catch: solar’s not perfect. It’s super dependent on the sun—so when it’s cloudy, when night hits, or even when the light dips a little, the power output drops like a rock. One minute you’re cranking out more electricity than you need, the next you’re scrambling to keep the lights on. And it’s not just a hassle for homeowners; that inconsistency messes with the grid’s frequency and voltage too, making it hard to use solar on a big scale.
The Core Idea: From “Passive Power” to “Active Control”
-
Solar First, Use What You Need
The solar panels (usually silicon ones) turn sunlight into DC power, which an inverter flips to AC—your standard household/business electricity. The system’s first move? Send that power straight to whatever you’re using right now—fridges, machines, computers, you name it. This way, you’re using as much of your own solar power as possible, cutting down on how much you buy from the grid. Win for your wallet.
-
Store the Extra (No More Wasting Power!)
When the sun’s shining bright and your solar panels are cranking out more power than you’re using? The system automatically shunts that leftover energy into a battery (most use lithium iron phosphate batteries—they’re safe and last forever). Think about it: if you’re at work all day, your solar system’s still making power—instead of that energy going to waste, it gets stored for when you get home and turn on the TV or cook dinner. No more “oh no, I missed out on free power!” moments.
-
Fill the Gaps When Solar’s Low
Now, when solar’s not cutting it—nighttime, cloudy days, or even if you suddenly crank up the AC and your power use spikes—the system switches gears. It pulls the stored energy from the battery to keep your power going. If you’re connected to the grid and the battery runs low? It’ll tap into the grid smoothly, no sudden blips. And if you’re off-grid (like in a remote cabin or a construction site)? That battery becomes your lifeline—no more relying on spotty grid access.
Why These Systems Fix Intermittency Better Than Separate Setups
| Aspect | Traditional Separate (Solar + Storage) | Solar-Storage All-in-One |
|---|---|---|
| Syncing | Solar and storage work on their own—slow to respond, often out of sync | One smart system controls everything—responds in milliseconds, matches generation and storage perfectly |
| Reliability | Gear from different brands (inverters, batteries) often clash—more breakdowns | Tested as a whole before it leaves the factory—hardware and software work together, 60% fewer issues |
| Installation & Maintenance | You need to plan separate spots for solar and storage, messy wiring; you have to call two companies for fixes | All-in-one design, smaller size—installation costs 30-50% less; one company handles all maintenance |
| Grid Friendliness | Solar’s ups and downs hit the grid directly—causes fluctuations | Smooths out solar’s peaks and valleys (“peak shaving, valley filling”)—sends steady power to the grid, less stress on it |
Where These Systems Shine (Literally!)
-
Homeowners: “My Power, My Way”
If you have a rooftop solar setup, pairing it with an all-in-one system is a no-brainer. Daytime: power your fridge, AC, and washing machine. Extra power? Stash it in the battery. Nighttime: use that stored power instead of paying the grid. Take an example from eastern China— a 10kW home system makes about 12,000 kWh a year. With storage, 80% of that gets used at home, saving over 5,000 yuan (around $700) in electricity bills annually. Plus, no more panicking when the grid goes out.
-
Businesses: Cut Costs, Keep Production Running
For factories or shops, electricity bills are a huge expense—especially when peak-hour prices are 3-4 times higher than off-peak. An all-in-one system fixes that. A manufacturing plant with a 500kW system, for example, uses solar during the day, stores the extra, then uses that stored power during evening peaks. That’s over 1 million yuan ($140,000) in savings each year. And if the grid goes down? The battery kicks in, so production doesn’t stop. No more costly downtime.
-
Remote Areas: “Finally, Reliable Power”
Think mountain villages, islands, or construction sites where the grid doesn’t reach. Before, these places relied on diesel generators—loud, smelly, and expensive. Now, an all-in-one system changes everything. A remote village in western China got a 200kW off-grid system, and suddenly they had 24/7 power. No more rationing, no more buying diesel. They can power homes and run small factories to process local crops. It’s not just power—it’s a boost for the whole community.
-
The Grid: A Helping Hand
Grid companies love these systems too. When thousands of them are connected, they act like a “distributed battery” for the grid. During summer heatwaves (when everyone’s using AC), the systems release stored power to ease grid stress. Late at night (when power use is low), they soak up extra grid power (or solar surplus) to avoid waste. Germany’s already doing this—hundreds of thousands of home systems are part of “virtual power plants” (VPPs) that the grid can control. It makes the grid more flexible, so it can handle more solar and wind power.
What’s Next? Bigger, Better, More Affordable
Wrapping Up
If you're interested in learning more about our solar energy storage offerings, we encourage you to explore our product line. We offer a range of panels and battery that are designed for various applications and budgets, so you're sure to find the right solution for your needs.
Website:www.fgreenpv.com
Email:Info@fgreenpv.com
WhatsApp:+86 17311228539
Post time: Sep-24-2025