As one of the core components of photovoltaic (PV) systems, inverters play a critical role. But what exactly do photovoltaic inverters do? How do they work? These questions might be confusing for newcomers to the solar industry. Today, we will explore the various aspects of inverters and their significance.
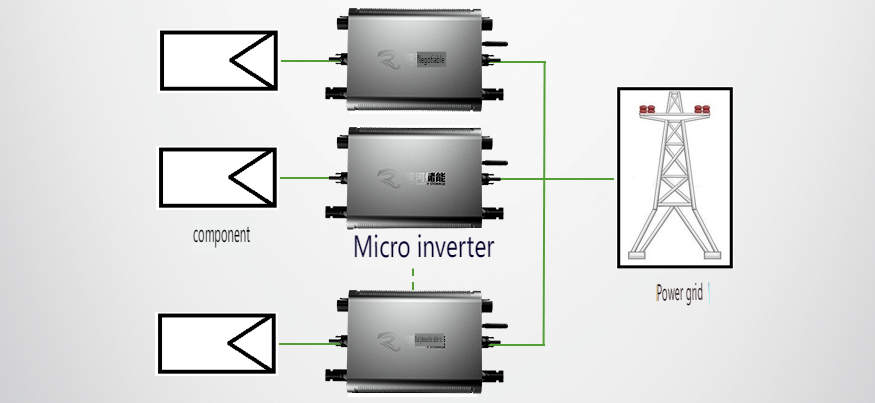
Microinverters
Microinverters are small inverters that are connected to each individual solar panel, each with its own Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) capability. This configuration allows for optimal performance of each panel, typically used in solar power systems ranging from 50W to 400W. Although microinverters generally have lower efficiency compared to string inverters, they offer several distinct advantages and are ideal for small residential systems or Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) projects.
**Advantages:**
1. **Simple Installation:** The modular installation approach simplifies the design and on-site installation processes, requiring just a single cable to connect to the distribution panel.
2. **Cost Savings:** With no need for a direct current (DC) section, related components are eliminated, reducing system costs and avoiding DC line losses.
3. **System Safety:** The absence of high DC voltage enhances safety, eliminating the risk of electrical shock and fire hazards. Unlike systems using central or string inverters where the DC voltage remains high even when the AC output is zero, microinverter systems have a low DC voltage of only 30-40V.
**Disadvantages:**
1. **Higher Cost Per Unit:** Microinverters tend to be more expensive than central and string inverters on a per-unit basis.
2. **Maintenance Costs:** Repairing or replacing microinverters can be costlier and more complex.
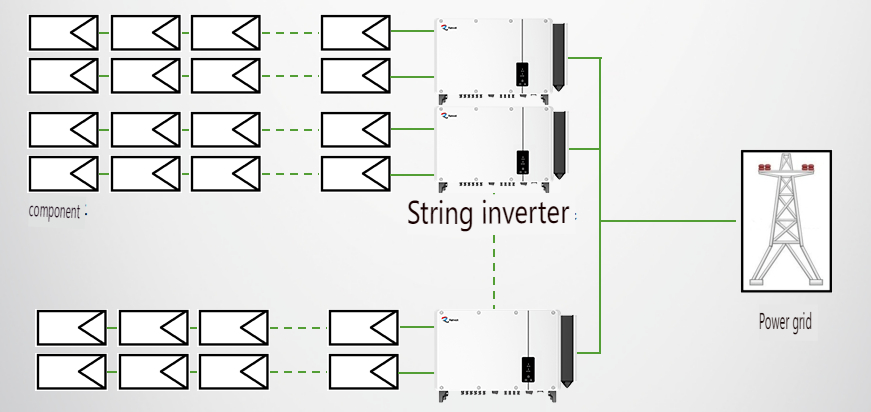
String Inverters
String inverters manage the power conversion for multiple strings of solar panels, each string typically consisting of several panels. These inverters are capable of independent MPPT for each string and are generally used in systems with capacities up to 320kW. String inverters are suitable for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and large-scale solar power plants.
**Advantages:**
1. **Reduced Mismatch Losses:** By minimizing the effects of module differences and shading, string inverters help increase overall energy yield.
2. **Cost Efficiency:** The technical advantages of string inverters, such as reduced system costs and increased reliability, make them cost-effective. They also require shorter DC cables, reducing shading losses and mismatch losses between different strings.
3. **Scalability and Flexibility:** String inverters are easy to scale and adapt to various system sizes and configurations.
**Disadvantages:**
1. **Higher Cost Compared to Central Inverters:** Although more cost-effective than microinverters, string inverters can be more expensive than central inverters.
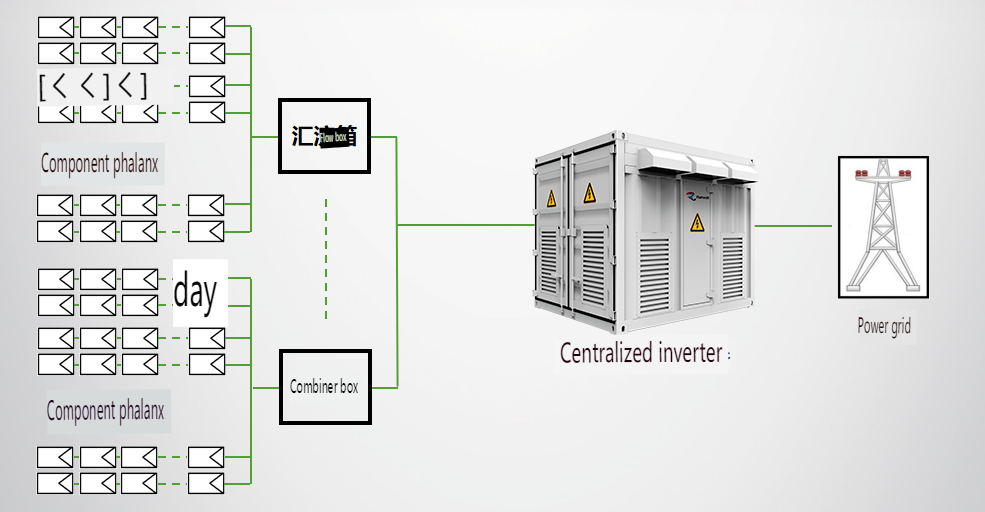
Central Inverters
Central inverters convert the DC power from numerous parallel-connected solar strings into AC power. These inverters are often large and come in containerized units, sometimes integrated with step-up transformers. Central inverters are typically used in large-scale solar power plants on flat terrain or large bodies of water.
**Advantages:**
1. **High Power Capacity:** Central inverters can handle high power loads, making them suitable for large installations.
2. **Cost-Effective for Large Projects:** Due to their high capacity and mature technology, central inverters offer low costs and good grid regulation capabilities.
**Disadvantages:**
1. **Sensitivity to Shading and Mismatch:** Central inverters require well-matched solar strings and are sensitive to shading and module mismatches. Issues like clouds, shadows from trees, or individual string failures can significantly impact system efficiency and energy production.
2. **Maintenance Challenges:** Maintenance can be more complicated, and the entire system can be affected by issues in a single string.
Conclusion
Understanding the types and functions of photovoltaic inverters is essential for optimizing solar energy systems. Each type of inverter—central, string, distributed, and micro—has specific advantages and is suited for different applications. Choosing the right inverter involves considering system size, location, and specific needs to ensure maximum efficiency and reliability. With the right inverter, solar power systems can effectively harness renewable energy, contributing to a sustainable future.
If you're interested in learning more about our solar energy storage offerings, we encourage you to explore our product line. We offer a range of panels and battery that are designed for various applications and budgets, so you're sure to find the right solution for your needs.
Website:www.fgreenpv.com
Email:Info@fgreenpv.com
WhatsApp:+86 17311228539
Post time: Jun-17-2024